Qatar Cars provides a more internationally-focused, modern cars-based
demonstration dataset. It mirrors many of the columns in
mtcars, but uses (1) non-US-centric makes and models, (2)
2025 prices, and (3) metric measurements, making it more appropriate for
use as an example dataset outside the United States. It includes almost
exactly the same variables as the mtcars dataset:
origin (the country associated with the car brand)make (the brand of the car, such as Toyota or Land
Rover)model (the specific type of car, such as Land Cruiser
or Defender)length, width, and height
(all in meters)trunk capacity (measured in liters)economy (measured in liters per 100 km)performance (time in seconds to accelerate from 0 to
100km/h)mass in kilogramsprice in 2025 Qatari riyalstype (the type of the car, such as coupe, sedan, or
SUV)enginetype (electric, hybrid, or petrol)The original data was compiled by Paul Musgrave in January 2025 and is mostly sourced from YallaMotors Qatar. See Paul’s writeup of the background and purpose of the data.
The Qatar Cars data is available in several different formats:
This {qatarcars} R package. See below for complete details. Load like this:
library(qatarcars)
qatarcarsPlain text CSV file. Use with any software.
Stata .dta file. Load like this:
use "qatarcars.dta"
list in 1/6R .rds file. Load like this:
df <- readRDS("qatarcars.rds")
head(df)The
QatarCars Python package. Install with
pip install qatarcars, then load like this:
from qatarcars import get_qatar_cars
df = get_qatar_cars("pandas") # or "polars"
df.head()The released version of {qatarcars} is available on CRAN:
install.packages("qatarcars")You can also install the development version from GitHub:
# install.packages("remotes")
remotes::install_github("profmusgrave/qatarcars")Similar to other data-only R packages like {gapminder} and {palmerpenguins},
load the data by running library(qatarcars):
library(qatarcars)
qatarcars
#> # A tibble: 99 × 15
#> origin make model length width height seating trunk economy horsepower
#> <fct> <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 Germany BMW 3 Seri… 4.71 1.83 1.44 5 480 11.8 184
#> 2 Germany BMW 3 Seri… 4.71 1.83 1.44 5 59 7.6 386
#> 3 Germany BMW X1 4.50 1.84 1.64 5 505 6.6 313
#> 4 Germany Audi RS Q8 5.01 1.69 2.00 5 605 12.1 600
#> 5 Germany Audi RS3 4.54 1.85 1.41 5 321 8.7 400
#> 6 Germany Audi A3 4.46 1.96 1.42 5 425 6.5 180
#> 7 Germany Mercedes Maybach 5.47 1.92 1.51 4 500 13.3 612
#> 8 Germany Mercedes G-Wagon 4.61 1.98 1.97 5 480 13.1 585
#> 9 Germany Mercedes EQS 5.22 1.93 1.51 5 610 NA 333
#> 10 Germany Mercedes GLA 4.41 1.83 1.61 5 435 5.6 163
#> # ℹ 89 more rows
#> # ℹ 5 more variables: price <dbl>, mass <dbl>, performance <dbl>, type <fct>,
#> # enginetype <fct>[!TIP]
If you have {tibble} installed (likely as part of the tidyverse),
qatarcarswill load as a tibble with nicer printing output; if you do not have {tibble} installed, the data will load as a standard data frame.
See ?qatarcars for data documentation within R.
Most columns in qatarcars are labeled:
attributes(qatarcars$economy)
#> $label
#> [1] "Fuel Economy (L/100km)"These labels are visible in RStudio’s Viewer panel:

If you use {ggplot2} v4.0+, these variable labels will automatically appear in plot labels:
library(ggplot2)
ggplot(qatarcars, aes(x = economy)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 1, fill = "#8A1538", color = "white")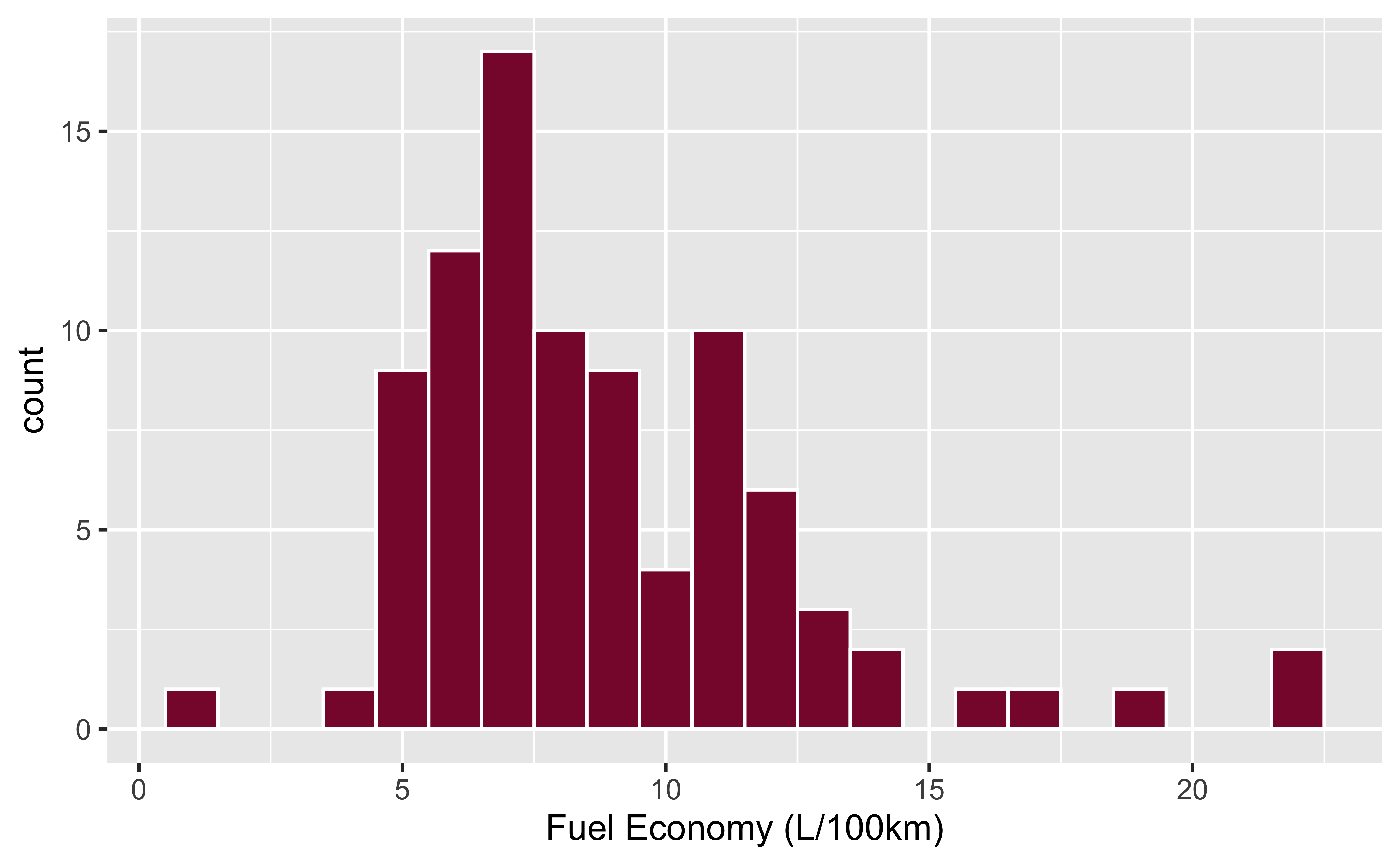
Fuel efficiency gets worse as cars get heavier:
ggplot(qatarcars, aes(x = mass, y = economy)) +
geom_point() +
geom_smooth(method = "lm") +
scale_x_continuous(labels = scales::label_comma())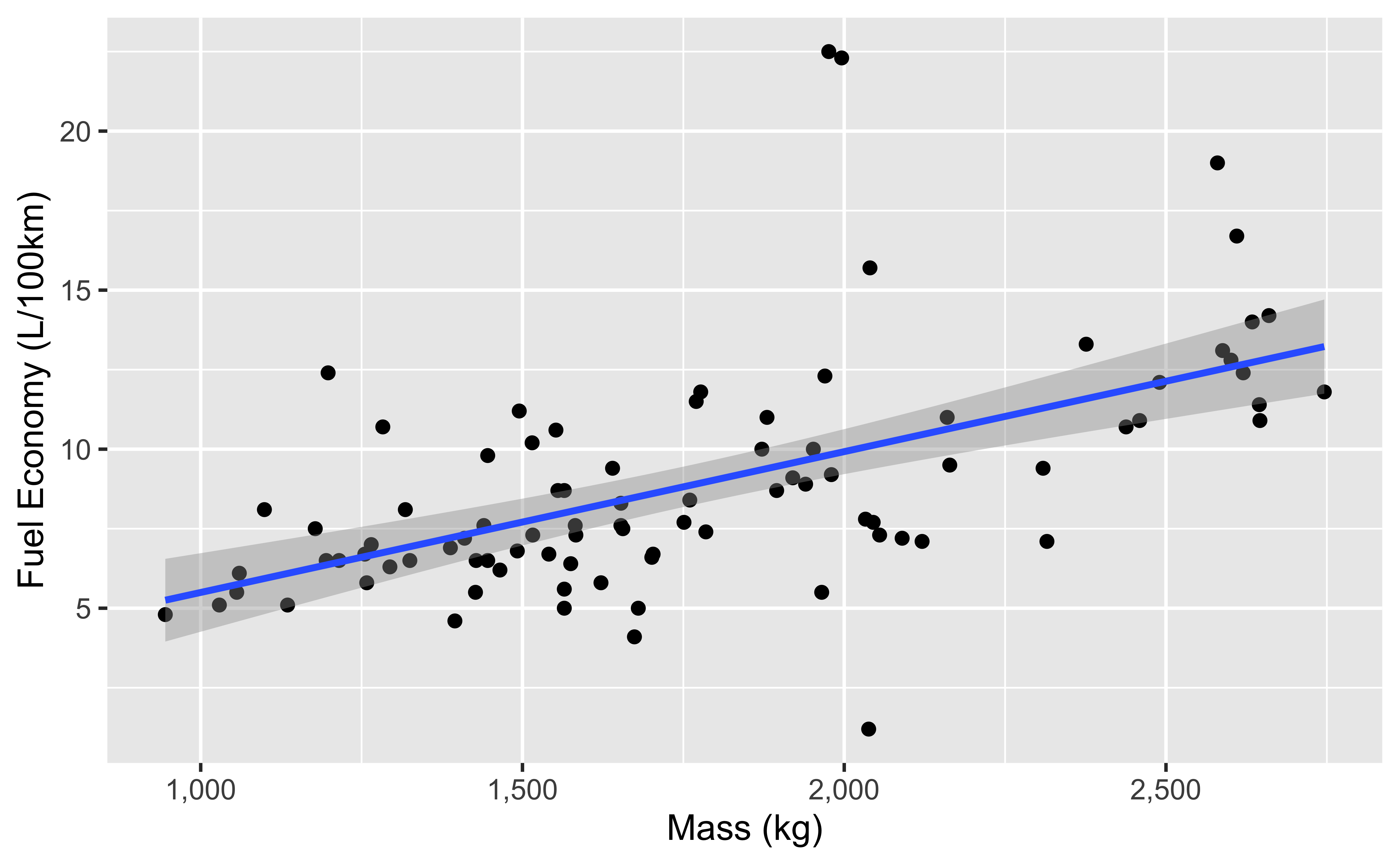
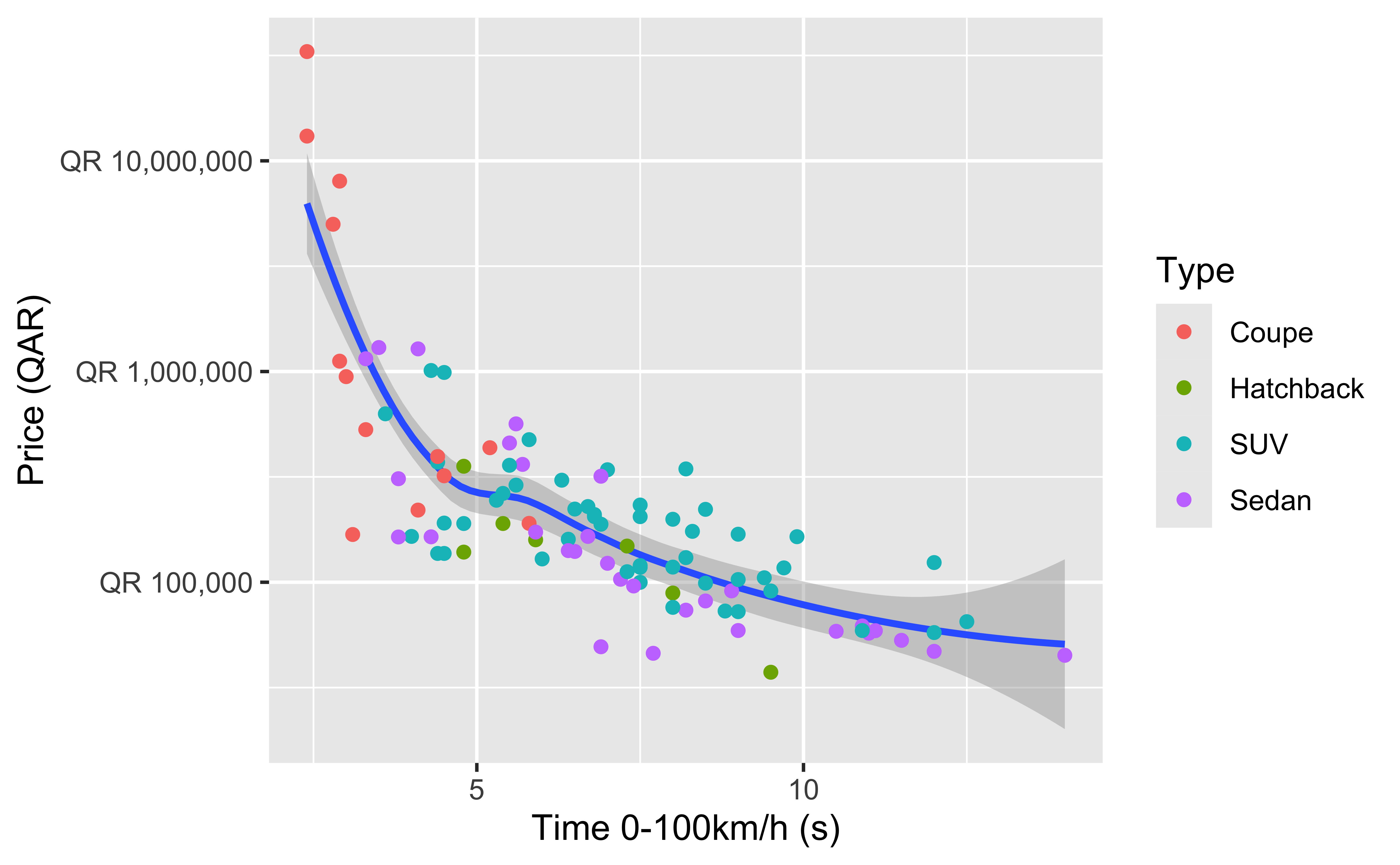
Some of these cars are really expensive, so logging the price is helpful:
ggplot(qatarcars, aes(x = performance, y = price)) +
geom_smooth() +
geom_point(aes(color = type)) +
scale_y_log10(labels = scales::label_currency(prefix = "QR "))